Firebase Cannot Read Property 'length' of Null - It Should Be Null
When using Firebase panel or the Remote Config backend APIs, you define one or more than parameters (key-value pairs) and provide in-app default values for those parameters. You can override in-app default values by defining server-side parameter values. Parameter keys and parameter values are strings, but parameter values tin be cast as other data types when yous use these values in your app.
Using the Firebase console or the Remote Config REST API, you can create new default values for your parameters, as well as conditional values that are used to target groups of app instances. Each time you update your configuration in the Firebase console, Firebase creates and publishes a new version of your Remote Config template. The previous version is stored, allowing you to retrieve or rollback as needed. These operations are also bachelor to you via the Residual API.
This guide explains parameters, weather condition, rules, conditional values, and how diverse parameter values are prioritized on the Remote Config Server and in your app. It also provides details on the types of rules used to create atmospheric condition.
Conditions, rules, and provisional values
A condition is used to target a group of app instances. Weather are made up of one or more than rules that must all evaluate to true for the condition to evaluate to true for a given app instance. If the value for a rule is undefined (for instance, when no value is available), that rule will evaluate to false.
For instance, a parameter that defines an app'southward splash page could display unlike images based on OS type using the unproblematic dominion if device_os = Android:
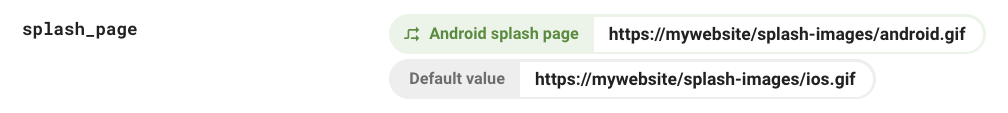
Or, a time condition could be used to command when your app displays special promotional items.
A parameter tin can accept multiple conditional values that use different weather, and parameters can share conditions within a project. In the Parameters tab of the Firebase panel, you can view the fetch percentage for each parameter's conditional values. This metric indicates the percentage of requests in the terminal 24 hours that received each value.
Parameter value priority
A parameter might have several conditional values associated with it. The post-obit rules determine which value is fetched from the Remote Config Server, and which value is used in a given app case at a particular point in time:
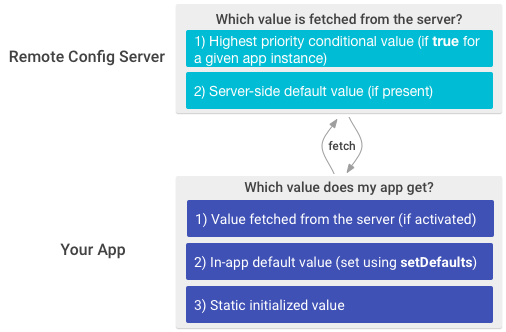
Server-side parameter values are fetched according to the following priority list
-
First, conditional values are applied, if any have conditions that evaluate to
truefor a given app instance. If multiple conditions evaluate totruthful, the first (superlative) i shown in the Firebase console UI takes precedence, and conditional values associated with that condition are provided when an app fetches values from the backend. You can alter the priority of conditions past dragging and dropping weather in the Conditions tab. -
If there are no conditional values with conditions that evaluate to
true, the server-side default value is provided when an app fetches values from the backend. If a parameter doesn't be in the backend, or if the default value is set to Use in-app default, so no value is provided for that parameter when an app fetches values.
In your app, parameter values are returned by get methods according to the following priority list
- If a value was fetched from the backend and then activated, the app uses the fetched value. Activated parameter values are persistent.
- If no value was fetched from the backend, or if values fetched from the Remote Config backend take non been activated, the app uses the in-app default value.
- If no in-app default value has been set, the app uses a static type value (such every bit
0forintandfalseforboolean).
This graphic summarizes how parameter values are prioritized in the Remote Config backend, and in your app:
Parameter value data types
Remote Config allows y'all to select a information type for each parameter, and validates all server-side values against that type before a template update. The information type is stored and returned on a getRemoteConfig asking.
The currently supported types are:
-
Cord -
Boolean -
Number -
JSON
In the Firebase console UI the data type tin be selected from a dropdown next to the parameter key. In the Balance API types tin can be set using the value_type field within the parameter object.
Parameter groups
Remote Config allows you lot to grouping parameters together for a more organized UI and mental model.
For instance, let'south say you need to enable or disable three different auth types while rolling out a new login characteristic. With Remote Config, you can create the three parameters to enable the types as desired, and then organize them in a group named "New login," with no demand to add prefixes or special sorting.
You can create parameter groups using the Firebase panel or the Remote Config Residue API. Each parameter grouping you create has a unique name in your Remote Config template. When creating parameter groups, keep in mind:
- Parameters can be included in but 1 group at whatsoever time, and a parameter key must however be unique across all parameters.
- Parameter group names are express to 256 characters.
- If you lot use both the REST API and the Firebase console, make sure that any Residual API logic is updated to handle parameter groups on publish.
Create or modify parameter groups using the Firebase console
Yous tin can group parameters in the Parameters tab of the Firebase console. To create or modify a grouping:
- Select Manage groups.
- Select checkboxes for parameters you want to add and select Motion to group.
- Select an existing group, or create a new group by entering a proper noun and description, and selecting Create new group. After y'all save a group, it is bachelor to be published using the Publish changes button.
Create groups programmatically
The Remote Config REST API provides an automated way to create and publish parameter groups. Assuming yous are familiar with REST and are fix upward to authorize requests to the API, you can perform these steps to manage groups programmatically:
- Remember the current template
- Add JSON objects to correspond your parameter groups
- Publish the parameter groups using an HTTP PUT asking.
The parameterGroups object contains group keys, with a nested clarification and list of grouped parameters. Annotation that each group cardinal must be globally unique.
For example, here is an excerpt from a template revision that adds the parameter group "new menu" with i parameter, pumpkin_spice_season:
{ "parameters": {}, "version": { "versionNumber": "i", … }, "parameterGroups": { "new menu": { "clarification": "New Menu", "parameters": { "pumpkin_spice_season": { "defaultValue": { "value": "true" }, "clarification": "Whether it's currently pumpkin spice season." } } } } } Condition rule types
The following rule types are supported in the Firebase console. Equivalent functionality is available in the Remote Config Residuum API, as detailed in the conditional expression reference.
| Rule blazon | Operator(southward) | Value(s) | Note |
|---|---|---|---|
| App | == | Select from a list of App IDs for apps associated with your Firebase project. | When you add an app to Firebase, y'all enter a parcel ID or Android package name that defines an attribute that'south exposed every bit App ID in Remote Config rules. Use this attribute every bit follows:
|
| App version | For string values: exactly matches, contains, does non contain, regular expression For numeric values: | Specify the version(due south) of your app to target. Earlier using this rule, you must use an App ID rule to select an Android/Apple app associated with your Firebase project. | For Apple tree platforms: Utilise the app's CFBundleShortVersionString. Note: Make sure your Apple tree app is using Firebase Apple tree platforms SDK version vi.24.0 or above, as CFBundleShortVersionString is non being sent in before versions (see release notes). For Android: Employ the app'south versionName. String comparisons for this rule are case-sensitive. When using the exactly matches, contains, does non contain , or regular expression operator, you tin can select multiple values. When using the regular expression operator, yous can create regular expressions in RE2 format. Your regular expression can match all or part of the target version string. You tin besides employ the ^ and $ anchors to match the outset, end, or entirety of a target cord. |
| Build number | For cord values: exactly matches, contains, does not incorporate, regular expression For numeric values: | Specify the build(southward) of your app to target. Before using this dominion, you must utilise an App ID rule to select an Apple or Android app associated with your Firebase project. | This operator is available for Apple and Android apps only. It corresponds to the app's CFBundleVersion for Apple and versionCode for Android. Cord comparisons for this rule are case-sensitive. When using the exactly matches, contains, does not incorporate , or regular expression operator, you lot can select multiple values. When using the regular expression operator, y'all tin can create regular expressions in RE2 format. Your regular expression tin can match all or part of the target version string. Yous can also use the ^ and $ anchors to match the beginning, end, or entirety of a target string. |
| Platform | == | iOS Android Web | |
| Operating organisation | == | Specify the operating system(southward) to target. Earlier using this rule, you must use an App ID rule to select a Web app associated with your Firebase projection. | This rule evaluates to truthful for a given Spider web app instance if the operating system and its version matches a target value in the specified list. |
| Browser | == | Specify the browser(s) to target. Before using this rule, you must use an App ID rule to select a Web app associated with your Firebase project. | This rule evaluates to truthful for a given Web app instance if the browser and its version matches a target value in the specified list. |
| Date/Fourth dimension | <=, > | A specified appointment and time, either in the device timezone or a specified timezone such as "(GMT+xi) Sydney fourth dimension." | Compares the current time to the device fetch time. |
| User in random percentile | <=, > | 0-100 | Use this field to utilise a change to a random sample of app instances (with sample sizes as small as .0001%), using the <= and > operators to segment users (app instances) into groups. Each app instance is persistently mapped to a random whole or partial number, according to a key defined in that project. A rule will utilise the default central (shown every bit DEF in Firebase panel) unless you lot select or create another key. You can return a rule to using the default key by clearing the Randomize users using this key field. Yous can employ a unmarried key across rules to consistently accost the same app instances within given percentage ranges. Or, you can select a new randomly-assigned group of app instances for a given percentage range by creating a new key. For example, to create two related conditions that each apply to a non-overlapping 5% of an app's users, you could have one condition include a <= 5% dominion, and another condition include both a > five% rule and a <= x% rule. To brand it possible for some users to randomly announced in both groups, use different keys for the rules in each condition. |
| User in audition | == | Select ane or more from a list of Google Analytics audiences that yous take set upwardly for your project. | This rule requires an App ID dominion to select an app associated with your Firebase project. Note: Because many Analytics audiences are defined past events or user properties, which can be based the actions of app users, information technology may take some fourth dimension for a User in audience rule to accept result for a given app instance. |
| Device in region/country | == | Select one or more regions or countries. | This rule evaluates to true for a given app instance if the case is in whatsoever of the regions or countries listed. The device country lawmaking is determined using the device'south IP accost in the request or the country lawmaking adamant by Firebase Analytics (if Analytics data is shared with Firebase). |
| Device language | == | Select one or more languages. | This dominion evaluates to true for a given app instance if that app instance is installed on a device that uses one of the languages listed. |
| User holding | For cord values: contains, does not contain, exactly matches, regular expression For numeric values: Note: On the customer, you tin set just string values for user properties. For conditions that apply numeric operators, Remote Config converts the value of the respective user holding into an integer/float. | Select from a list of available Google Analytics user properties. | To learn how you lot can employ user backdrop to customize your app for very specific segments of your user base, see Remote Config and user properties. To learn more than about user properties, see the post-obit guides:
When using the exactly matches, contains, does not contain or regular expression operator, you can select multiple values. When using the regular expression operator, you can create regular expressions in RE2 format. Your regular expression tin can match all or part of the target version string. Y'all can also use the ^ and $ anchors to match the start, end, or entirety of a target string. Note: Automatically collected user backdrop are non currently available when creating Remote Config atmospheric condition. |
| Imported segment | == | Select one or more imported segment. | This dominion requires setting up custom imported segments. |
| Installation ID | == | Specify one or more Installation IDs (up to fifty) to target. | This rule evaluates to truthful for a given installation if that installation'southward ID is in the comma-separated list of values. To larn how yous can become installation IDs, see Call up client identifiers. |
Searching parameters and conditions
You tin search your project'southward parameter keys, parameter values, and weather from the Firebase console using the search box at the superlative of the Remote Config Parameters tab.
Limits on parameters and conditions
Within a Firebase project, y'all can have up to 2000 parameters, and up to 500 atmospheric condition. Parameter keys can exist upwardly to 256 characters long, must outset with an underscore or English letter graphic symbol (A-Z, a-z), and may too include numbers. The total length of parameter value strings within a project cannot exceed 1,000,000 characters.
Adjacent steps
To get started configuring your Firebase project, encounter Set up a Firebase Remote Config Projection.
Source: https://firebase.google.com/docs/remote-config/parameters
0 Response to "Firebase Cannot Read Property 'length' of Null - It Should Be Null"
Post a Comment